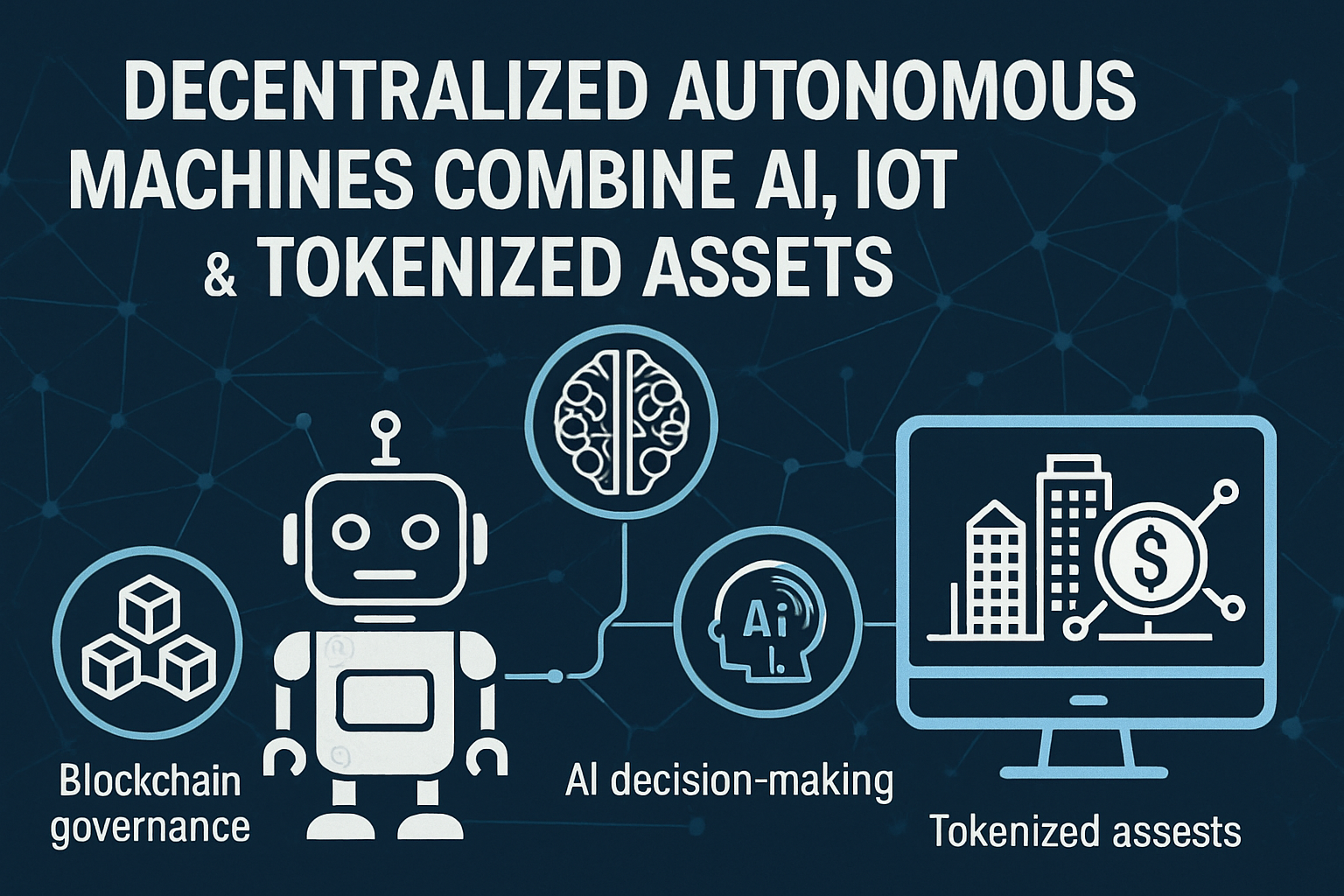
In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital transformation, a new category of autonomous infrastructure is beginning to take shape: Decentralized Autonomous Machines (DAMs). These entities represent the convergence of three powerful technologies — Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and Tokenized Assets — all governed by decentralized protocols built on blockchain.
What Are Decentralized Autonomous Machines?
At their core, DAMs are systems that can operate independently without human intervention. Unlike traditional automation, these machines don’t just follow pre-set scripts; they leverage AI for adaptive decision-making, IoT for real-world data sensing and interaction, and blockchain for decentralized governance and financial autonomy.
A DAM can be a physical robot or sensor network — such as a drone fleet, agricultural machine, or logistics robot — or a digital agent managing cloud infrastructure or trading tokenized assets. What ties them all together is their trustless, decentralized nature and self-sufficiency in managing resources and executing tasks.
How It Works: A New Tech Stack
-
IoT Devices
Sensors and edge devices serve as the physical interface with the environment, collecting and transmitting data in real time. -
AI Decision-Making
Embedded machine learning models process incoming data, adapt to changing conditions, and make operational decisions, such as adjusting irrigation in a smart farm or rerouting a delivery bot. -
Blockchain Governance
All decisions and transactions are governed transparently via smart contracts. DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations) can vote on upgrades or maintenance, and on-chain rules prevent tampering or central control. -
Tokenized Assets
These machines can own and trade digital assets. For example, a solar-powered DAM could sell excess energy in a DePIN (Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network), pay for maintenance via crypto, or reward contributors with tokens.
Real-World Examples
-
Autonomous Delivery Bots
Connected to IoT sensors and GPS, governed by DAO logic, and financed via micro-payments in crypto. -
AI-Powered Agriculture Machines
These can measure soil quality and climate, decide when and where to water or harvest, and log actions transparently on-chain. -
Tokenized Smart Infrastructure
Smart buildings or grid systems that make their own decisions based on usage data, with energy credits or access rights tokenized and tradable on DePIN platforms.
Why It Matters
The potential of DAMs lies in their scalability, transparency, and decentralization. Unlike traditional corporate-owned infrastructure, DAMs shift control to users and communities, reduce operational overhead, and enable programmable business models. This unlocks new paradigms for sectors like:
-
Energy (DePIN)
-
Logistics & Mobility
-
Agriculture
-
Finance (DeFi + Tokenized Machines)
DAMs also represent an evolution of Web3 logic: instead of just decentralizing data or money, we’re decentralizing machines themselves — giving rise to a machine economy that is autonomous, tokenized, and trustless.
The Challenges Ahead
Like any revolutionary concept, DAMs face technical and regulatory hurdles:
-
Ensuring AI transparency and accountability in decision-making.
-
Reliable on-chain/off-chain communication via oracles.
-
Hardware security and resilience of IoT networks.
-
Legal recognition of machine-owned assets or DAOs.
Nonetheless, with momentum building — including mentions in Wall Street Journal, arXiv preprints, and Financial Times — the DAM concept is attracting serious attention from researchers, builders, and investors alike.
The fusion of AI, IoT, and tokenized infrastructure marks a new frontier in digital autonomy. Whether it’s decentralized smart grids, intelligent supply chains, or token-managed robots, Decentralized Autonomous Machines promise a world where machines work for us — but answer to no one.